What's DDR5 & DDR4?What are the differences between them?
What exactly are DDR5 and DDR4? What are the differences between them? And what's going on with this price increase?
What is DDR? In simple terms, DDR is the abbreviation for "Double Data Rate" memory. You can think of it as a super-fast temporary data storage station in a computer, where all the data processed by the CPU must pass through first. The numbers 4 and 5 at the end represent its "generation", just like the difference between iPhone 14 and 15.
DDR5 is the next generation and is more advanced than DDR4. So what exactly makes it "new"? Here are some examples:
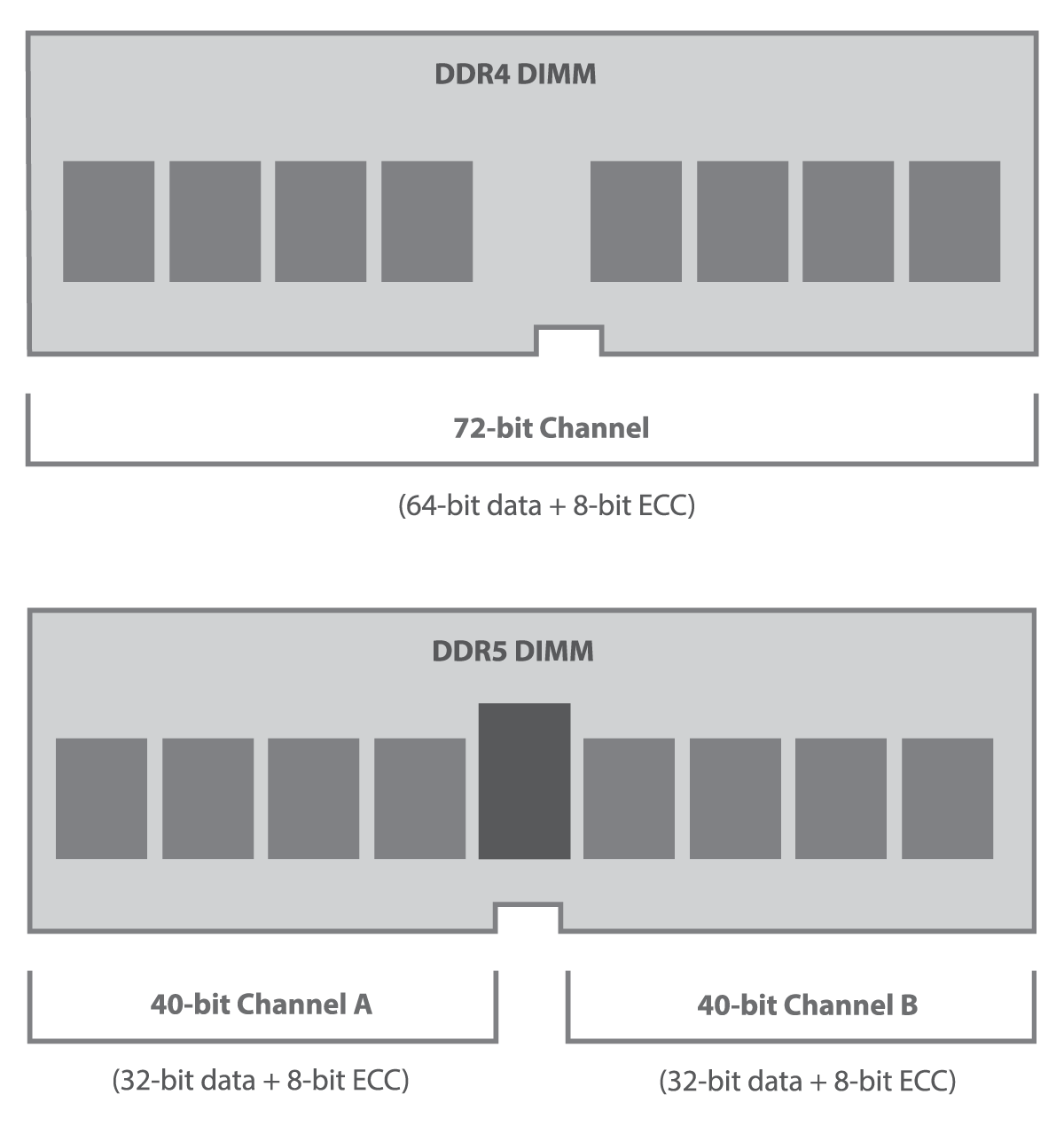
A single memory module of DDR4 is a 64-bit channel, while a single memory module of DDR5 is internally divided into two separate 32-bit sub-channels.

The driving force behind DDR5:
The widening gap between processor performance and memory bandwidth remains the fundamental driving force behind the dominance of DDR5. By 2025, the number of processor cores will increase explosively; we can now see that the server CPUs of AMD (EPYC Turin) and Intel (Xeon 6) each have up to 192 and 288 cores per slot respectively. In such ultra-high-core systems, the single-core bandwidth provided by the outdated DDR4 technology is far from sufficient.
From an application perspective, the large-scale adoption of DDR5 is attributed to the following factors: ① The widespread use of AI-native PCs and super-large-scale servers; ② The urgent need for massive bandwidth to train and run large language models (LLMs); ③ Comprehensive platform support provided by major manufacturers including AMD, Intel, SK Hynix, Samsung, and Micron.
Advantages of DDR5:
1.Provide more than double the effective bandwidth
2. The Next-Generation Memory for Transforming Data into Insights
3. Support for the memory technology of Intel's new generation server platform
4.The operating voltage of DDR4 is 1.2 volts, while that of DDR5 is 1.1 volts. Lower operating voltages can significantly reduce power consumption.
5.In October 2022, AMD launched the fourth generation EPYC processors, and in January 2023, Intel introduced the fourth generation Xeon processors. Both of these products support DDR5 memory.
![]()
Memory technology has evolved from DDR3 and DDR4 to the new generation DDR5. In 2025, DDR4 will remain an important choice due to its maturity and high cost-effectiveness. DDR5 represents the future direction and is accelerating its adoption. Both technologies coexist in the market.
The early DDR5 versions had higher latency. However, the current mainstream high-frequency DDR5 kits have adopted optimized timing, and their actual latency is comparable to, or even lower than, that of a good DDR4 kit.
DDR5 memory represents the cutting-edge of current memory technology. Compared with DDR4, it has made significant advancements in frequency, transmission rate, bandwidth potential, per-module capacity limit, power management, and architecture design. These improvements provide a more solid foundation for high-performance computing, large-scale application processing, and professional creation. In 2025, for users building new PCs, especially those who pursue high performance, high productivity, or future upgrade space, choosing the DDR5 platform is undoubtedly a more forward-looking decision. It can better unleash the potential of new hardware. Meanwhile, DDR4, with its mature ecosystem, outstanding cost-effectiveness, and advantages in specific application scenarios, still maintains strong competitiveness in the market. For budget-sensitive users, mainstream application users, gamers using old platforms, or users upgrading from the existing DDR4 platform, DDR4 remains an economical and practical choice. It can fully meet daily and mainstream performance requirements.




